AI’s Deep Revolution in Marketing: Impact, Challenges, and the Human-AI Future
- On August 8, 2025
- AI marketing
AI is fundamentally reshaping the marketing landscape, moving it from a mere “efficiency tool” to a “strategic hub.” This shift is driven by AI’s ability to autonomously generate creativity, optimize (placement/campaigns), and predict consumer trends. The impact is felt across the entire marketing value chain, leading to significant cost reduction and efficiency gains, enhanced user experiences, and superior market insights and decision-making. However, this transformation also brings challenges, including intensified competition leading to market consolidation by tech giants, the emergence of a “digital divide” for smaller businesses, a paradigm shift in traffic acquisition through Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), and crucial ethical dilemmas around data privacy, truthfulness, and potential algorithmic manipulation. The future of AI marketing points towards a “symbiotic marketing” ecosystem, where multi-agent AI systems and predictive marketing become commonplace, pricing models shift to “result-as-a-service” (RaaS), and human roles are redefined to focus on strategy, emotion, and ethics.
1. AI’s Fundamental Restructuring of the Marketing Value Chain
AI is not merely improving existing marketing processes; it is “reconstructing the marketing value chain.” The market for AI marketing is rapidly expanding, with an estimated scale of 66.9 billion RMB in 2025 and projected to exceed 100 billion RMB by 2030, reflecting a 26.2% CAGR.
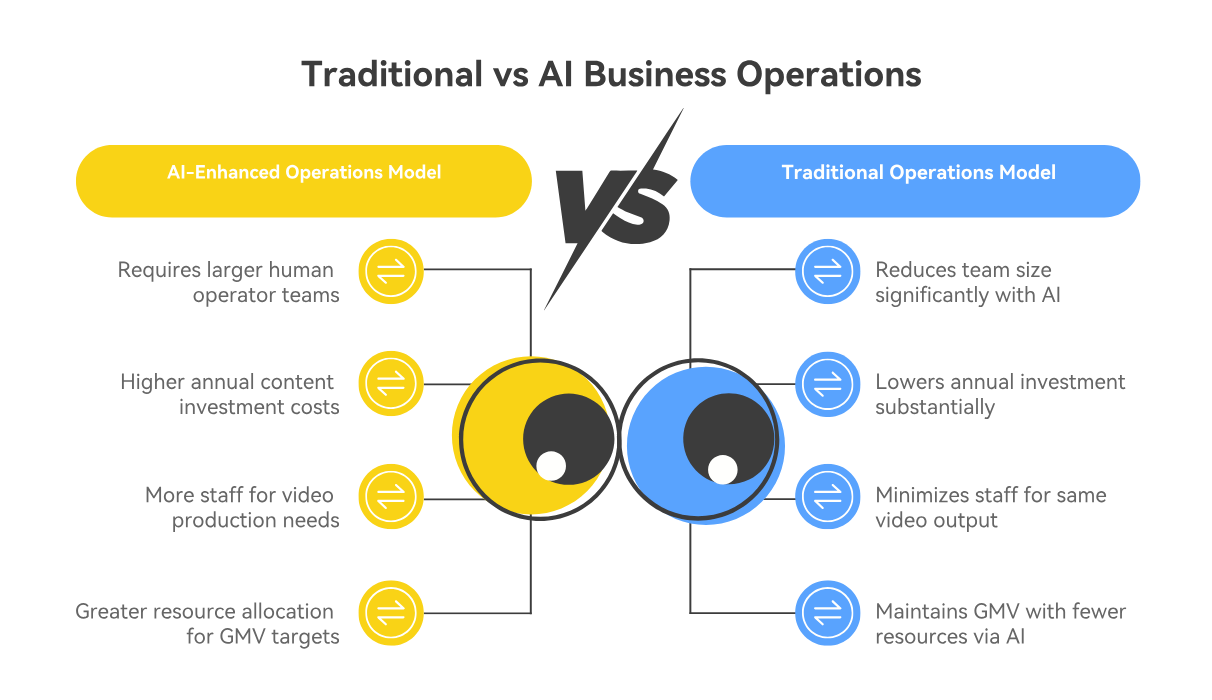
A. Cost Reduction and Efficiency Enhancement AI significantly reduces operational costs and boosts efficiency:
- Operational Team Size: A typical 1 billion GMV (Gross Merchandise Volume) store previously required 10-15 human operators and 2 million RMB annually for content. Now, “only 2-3 people + 100,000 level AI tool investment” can achieve the same scale.
- Video Production: AI can “compress 90% of the cost” for short video production, user interaction, and sales conversion. For example, a traditional MCN agency producing 8,000 videos monthly needed 7-8 people, but with AI, this is “now reduced to 2 people.”
– Specific Examples:”Digital Human Luo Yonghao” achieved 55 million GMV and 13 million views in a 618 Baidu livestream, with AI calling upon knowledge 13,000 times and generating 97,000 characters of product explanation.
– An NBA Finals AI-generated advertisement cost “2,000 USD, 48 hours,” a cost reduction of “over 95%.”
– Alimama’s AIGC creative capabilities helped “over 2 million merchants increase creative material efficiency,” with “AI image-to-video” and “AI instant film” boosting CTR by “up to 170%.”
B. Upgrading User Experience AI enables deeply personalized and interactive user experiences:
- Co-creation and Personalization: The McDonald’s “AI Cultural Relic Recreation Contest” example showed how AI allows users to “freely choose materials… to generate exclusive cultural relics, achieving personalized brand symbol fission.”
- Real-time Interaction: AI transforms traditional “brand one-way output” into “mass co-creation,” fostering real-time interaction.
- Predictive Understanding: AI can analyze user preferences to “predict the viral potential of cultural trends,” elevating brands beyond mere product symbols.
C. Market Insights and Decision-Making AI’s analytical capabilities drive smarter content and marketing strategies:
- Netflix’s Intelligent Closed-Loop: Netflix uses AI to analyze “over 95 billion hours of user viewing data,” enabling “data-driven creative decisions.” This includes identifying popular genre combinations (e.g., “dystopian + family ethics” for The Glory) and predicting global trends (e.g., “violent aesthetics” in Squid Game).
- Personalized Content Delivery: Netflix leverages AI for “thousand-person, thousand-face personalized experience,” dynamically generating tailored cover art and trailers. This strategy has contributed to “over 95 billion hours of viewing time.”
- Improved Business Outcomes: Netflix’s Q2 revenue was 11.08 billion USD (up 16%), with profit at 3.13 billion USD. Its advertising business saw “global monthly active users reach 94 million,” doubling year-on-year. Ad effectiveness showed “8 times higher brand favorability, 162% higher sales conversion, and 3 times higher purchase intent.”
2. AI Marketing Technology Evolution and Application
AI marketing has evolved through three stages:
- Phase 1 (2015-2020): Rule-engine dominant (e.g., Facebook’s precise targeted ads).
- Phase 2 (2021-2023): Generative AI breakthrough (e.g., ChatGPT writing ad copy).
- Phase 3 (2024-): Multi-Agent Collaboration (e.g., Amazon’s “demand prediction-production-logistics” closed-loop system).
This signifies a “paradigm shift from ‘single-point intelligence’ to ‘systemic collaboration’.” AI marketing now covers the entire marketing chain, including “insight automation, strategy generation, multi-modal content generation, intelligent placement and optimization, and effect attribution.” Content generation and intelligent placement are particularly prominent.
Alimama (Alibaba’s digital marketing platform) as an example:
- Marketing Insights: Uses AI for “opportunity人群 (target audience)-brand assets-conversion path” models, identifying high-potential customer groups. Midea Air Conditioners saw a “40% increase in store ROI” during 618. “Goods full-site push” automatically selects products with GMV growth potential.
- Content Generation: “One-click intelligent release of content productivity” from images to videos. “AI image-to-video” allows up to 10 images to quickly generate a video.
- Placement Optimization: Uni Desk’s dynamic material optimization and cross-media frequency control. “Net transaction bidding” reduced refund rates by “18%.”
- Effect Analysis: Uni Desk manages the “full life cycle of brand awareness, search, transaction, and repurchase.”
AI marketing is “widely penetrating” industries like gaming, FMCG, finance, and cross-border e-commerce, with “multi-Agent collaboration” becoming standard in the latter two due to extensive user data and short conversion paths.
3. Market Consolidation and Ecosystem Restructuring
A. Supply-Side Power Dynamics: Winner-Takes-All Cloud giants (e.g., Amazon, Microsoft), AI platforms (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic), and large media platforms (e.g., Google, Meta, ByteDance) are forming “strong monopolistic capabilities” due to their “absolute advantages in technology, data, computing power, and ecosystem.”
- Amazon’s Vertical Integration: Possesses strong cash flow (113 billion USD operating cash flow), substantial cash reserves (94 billion USD), and massive capital expenditure (24.3 billion USD in Q1 2025, 100 billion USD planned for 2025) primarily for AI. This integration spans from foundation models (Nova) to chip sales (Trainium), infrastructure (Bedrock), and applications (Alexa, advertising). Its advertising business grew “19% to 13.9 billion USD” in Q1.
- Tencent’s Dominance in China: With WeChat and QQ, Tencent commands “billions of real-time user behavior data and traffic entry points,” “significantly squeezing the survival space for small and medium-sized marketing service providers.”
Small and medium-sized (SMEs) marketing service providers face severe challenges: “technological homogeneity, intensified customer loss, and shrinking financing channels.” Many rely on open-source models, offering “single-point tools” that lack multi-agent capabilities. Survival strategies include “shifting to vertical domains and professional Agent transformation” or “deepening into regional markets” (e.g., ShuShangYun in Southeast Asia).
B. Demand-Side Digital Divide: Stratified Brand World
- Leading Brands Embrace AI: “Accelerating digital adoption,” either by building in-house AI capabilities or “deeply collaborating with top platforms.” Examples include L’Oréal’s CREAITECH lab and Nike acquiring Celect for a private demand prediction engine. These brands are becoming “rule co-conspirators,” reshaping traffic allocation and industry discourse.
- SMEs Become “Free Data Fuel”: Limited by data volume, SMEs struggle to leverage AI effectively, leading to poor marketing outcomes and potentially “淪為平台的免費數據燃料” (becoming free data fuel for platforms). AI “further widens the ‘digital divide’ caused by resource disparities.”
C. Traffic Entry Point Migration: GEO Becomes Mainstream Generative Engine Optimization
(GEO) is emerging as AI search becomes the primary way people access information. First formally proposed in a 2024 paper, GEO differs from traditional SEO:
- Target: GEO targets generative AI engines (ChatGPT, DeepSeek), aiming for content to be “prioritized in AI-generated direct answers,” unlike SEO which focuses on link rankings.
- Optimization Means: GEO emphasizes content “structuring, authority,” and semantic relevance for AI, while SEO focuses on website structure and keywords.
- Result Presentation: GEO-optimized content is “directly integrated into AI-generated structured answers,” unlike SEO which provides link lists.
The global AI search engine market is projected to reach 43.63 billion USD in 2025 and 108.88 billion USD by 2032, with a 14% CAGR. Generative AI will dominate the technology layer (54.2%).
Winners in the GEO revolution:
- Open AI Platforms: Control information sources and can directly recommend brands, potentially enabling “demand description → transaction closed-loop” (e.g., Amazon’s “Buy for Me”).
- Social Ecosystems: Super apps like TikTok and WeChat offer “scenario-based entry points” with immersive recommendation engines (e.g., TikTok Shop’s “video keyword + AI narration” triggering purchases).
- Vertical GEO Service Providers: Startups like “Profound” which saw its monthly AI search queries exceed “100 million” by June 2025, and increased client brand share in AI answers by “25%-40% within 60 days.”
However, GEO startups face “double pressure”: from transforming traditional SEO companies and “deep conflict with large model platforms.” Their “reverse engineering” approach makes them vulnerable to “highly opaque” and “weekly” algorithm updates from large models, leading to “blurred effect attribution.”
GEO’s “Power Black Box” Concerns:
- Platform Algorithmic Hegemony: Brands could “manipulate AI’s judgment of ‘authority’,” creating a “digital strong arm.”
- Capital-Driven Information Monopoly: Large brands may “monopolize core professional information sources” through massive budgets, making it difficult for SMEs to be seen by AI.
- “Double Black Box” Risk: If AI platforms silently introduce “bid-for-recommendation” (like ad slots) while blurring the mechanism, users might receive “soft ads” disguised as neutral information, potentially leading to critical issues in areas like healthcare.
D. Business Ecosystem Restructuring: Traditional vs. New Forces
Marketing is no longer exclusive to traditional advertising agencies. Tech giants are building new ecosystems (Meta aiming for full AI advertising by 2026). This is “squeezing the living space for traditional 4A companies,” leading to “revenue shrinkage, market share decline,” and necessitating “layoffs, business contraction, mergers, and transformations.”
WPP’s Struggle and AI Bet: WPP’s 2024 revenue fell by “0.7% to 18.426 billion USD,” with significant declines in China (-20.8%). They lost major clients and reduced staff by “6,129 people” by the end of 2024. WPP views AI as critical for survival, investing “over 400 million GBP annually” in AI, including a partnership with Nvidia for an AIGC content engine, and developing WPP Open and Open Intelligence. This signifies a shift from “human-intensive creativity” to “AI industrial production.”
Emergence of New Service Providers:
- Vertical AI Agent Companies: Navos (launched at WAIC 2025) focuses on full-chain cross-border marketing, potentially completing a traditional 4A project in “three days” that would take “three months,” boosting human resource efficiency “tens of times.”
- Youche Technology: Provided a full-chain AI marketing service for Chery’s Exeed, creating an ad in “10 days” (vs. 6-8 weeks traditionally) at a “fraction of the cost.”
- Independent AI Creative Studios: Rising due to AI lowering technical barriers and costs.
- Keling’s “Lingdong Huabu” platform allows individual creators to “independently complete multi-modal marketing content that previously required a 10-person team.” Keling AI has “over 45 million creators globally.” The core shift is AI handling execution, allowing humans to focus on higher-value insights, creative ideation, and strategy. “A few-person independent AI creative studio is expected to become the industry norm.”
4. Human-Machine Collaboration: Job Transformation and Evolution
AI is transforming work, with Microsoft’s CTO predicting “95%” of code will be AI-generated by 2030. In marketing, “basic execution roles” like copywriters, designers, data analysts, and placement optimizers will be “highly replaced.” However, this is a “turning point, not an end.”
- Executors to Strategists/Architects: Focus on “marketing insights, value proposition, emotional shaping,” areas AI struggles with.
- Executors to AI Trainers/Optimizers: Use industry knowledge to “train and optimize AI models” for more accurate and brand-aligned output.
This shift “pushes unique human values — creativity, strategic thinking, emotional connection — to the core.” The biggest risk is not being replaced by AI, but “sticking to old models” and refusing human-machine collaboration.
Organizational structures will evolve:
- Cross-functional Agile Teams: Integrating marketing, tech, and data.
- Universal AI Literacy: Making AI tool application and data insight core competencies.
Accelerated HR Offshore Outsourcing: Example: “AI review outsourcing centers” in Manila, Philippines, employing “over 100,000” content reviewers for tech companies.
5. AI Marketing Boundaries and Ethics
Beneath the surface of AI marketing’s prosperity lie “deep ethical dilemmas and value breakdowns.”
- Data Sovereignty and Regulatory Challenges: ChatGPT’s data leakage in March 2023, exposing sensitive user info and using it for training without authorization, led to a “15 million Euro GDPR fine.” Lawsuits by authors also highlight “copyright ownership and data usage regulatory blind spots.”
- Sacrifice of Emotional Warmth: While AI customer service boosts efficiency (87% of Hong Kong brands deploy it, 67% of businesses recognize efficiency), “only 17% of consumers felt brands achieved personalized interaction,” and “74% of local consumers would abandon purchases due to AI customer service not being ‘human’ enough.”
- “Truthfulness Trap” and Trust Crisis: Low-cost AI digital humans (5,000 RMB/set) can be optimized with “lonely elderly scripts” to “precisely induce elderly groups to purchase inferior goods.” This represents a “crushing of human values by technical rationality.”
- GEO as an “Algorithmic Monopoly” Tool: A leading building materials company manipulated AI recommendations for “top ten waterproof material brands” through whitepapers, creating an “algorithmic information cocoon” that misleads consumers and stifles SMEs.
- Algorithmic Hegemony and Fairness Imbalance: “The ‘power black box’ of GEO’s algorithmic operations must be highly vigilant.”
The limitations of AI marketing are not tool failure, but “the systematic silencing of humanity within algorithms.” When technology becomes a business creed under the banner of “cost reduction and efficiency,” human emotion, creativity, and ethical judgment are marginalized.
6. The Future: Symbiotic Marketing Ecosystem
To overcome data sovereignty issues, emotional detachment, and algorithmic hegemony, the future of AI marketing lies in a “symbiotic marketing” system where human wisdom, warmth, and ethics are central, and AI serves as an empowering engine.
A. Multi-Agent Collaboration as Marketing Infrastructure: Multi-agent AI is becoming foundational, transforming the industry’s underlying logic. The market for AI Agent marketing and sales is projected to reach 44.2 billion RMB in 2024 and will show “explosive growth” to “trillions of RMB” in the next five years.
Tencent AI Marketing Agent Matrix: Covers the full marketing chain from “market insights to placement optimization,” achieving “fully automated closed-loop.” Agents like Yi Analysis, Miaosi, ADQ, Miaobo, Miaowen, and Qidian Marketing Cloud collectively form an “autonomous collaborative AI Agent network.”
B. Widespread Predictive Marketing: Predictive marketing is becoming commonplace. Meta and University of Washington’s “PrefPalette” (July 2025) can not only “predict user behavior” but also “clearly explain its reasoning logic,” achieving an average accuracy of “84.9%” (46.6% higher than GPT-4o) in Reddit communities. It is more accurate in “academically strong communities” (91.6%) due to clear norms. Its “interpretability” is a major highlight.
C. Reshaped Pricing Models: “Result as a Service” (RAAS) models, already adopted by Youche Technology and TaiDong Technology, are gaining traction. This means directly delivering “measurable marketing results” rather than just SaaS tools. AI makes marketing effects “more quantifiable and predictable,” pushing “Performance-Based Pricing” to become mainstream. This signifies a shift from “selling tools” to “selling results,” and from a “resource-intensive” (budget, channels) to a “capability-intensive” (data closed-loop, results delivery) industry.
D. Redefining Human Roles: As AI handles efficiency, human value is re-anchored in “strategic lighthouse, emotional cradle, and ethical compass.” AI frees up human creativity, as seen with Keling AI’s 45 million creators.
- Humans as “Soul Architects”: Defining brand essence, long-term vision, and stable values.
- Humans as “Cultural Decoders”: Interpreting collective emotions, cultural norms, and intergenerational anxieties for AI.
- Humans as “Moral Calibrators”: Setting boundaries against algorithmic bias and commercial temptation, safeguarding brand values and social contracts.
AI marketing is a “deep revolution” touching industry foundations, power structures, work nature, and ethical boundaries. It involves efficiency gains, cost restructuring, giant monopolies, digital divides, job displacement, capability evolution, and ethical constraints. “Embracing technology while adhering to human strategic foresight, emotional connection, and ethical bottom line” is crucial for building a “solid foundation for human-machine symbiosis.” In this AI marketing revolution, humans are not replaced, but “re-anchor their irreplaceable value coordinates” against the backdrop of AI’s efficiency.

 Unlock 2026's China Digital Marketing Mastery!
Unlock 2026's China Digital Marketing Mastery!